Investing in bonds has long been a cornerstone of a balanced investment portfolio. Bonds provide stability, income, and a safer alternative to equities, especially for conservative investors or those nearing retirement. However, the bond market can be complex, with various maturities, interest rate risks, and credit qualities to consider. One effective strategy that can help navigate these challenges is bond laddering. This approach offers a systematic way to manage interest rate risks, ensure regular income, and maintain portfolio flexibility.
What is Bond Laddering?
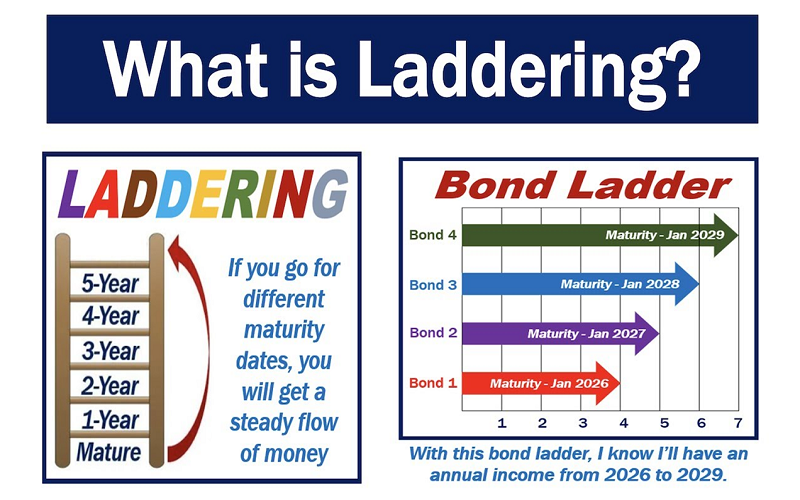
Bond laddering is an investment strategy that involves purchasing bonds with different maturity dates, spreading the investment across a range of time horizons. The idea is to create a “ladder” of bonds that mature at regular intervals. As each bond matures, the investor can reinvest the principal into a new bond at the top of the ladder (a longer maturity), or use the proceeds for other financial needs. This strategy helps to spread out interest rate risk and ensures a steady stream of income.
For instance, an investor might buy bonds that mature in 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 years. As the 1-year bond matures, the proceeds could be reinvested in a new 10-year bond, while the 3-year bond has two years left, and so on. This process continues, creating a self-sustaining cycle of maturity and reinvestment.
Benefits of Bond Laddering
- Mitigating Interest Rate Risk: One of the biggest challenges in bond investing is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds tends to fall because new bonds are issued at higher rates, making older, lower-yielding bonds less attractive. Conversely, when interest rates fall, existing bonds with higher rates become more valuable. By holding bonds with varying maturities, bond laddering reduces the impact of interest rate fluctuations. If rates rise, only a portion of the portfolio will be affected, and maturing bonds can be reinvested at higher rates. If rates fall, the longer-term bonds in the ladder continue to yield higher returns.
- Steady Income Stream: Bond laddering provides a predictable income stream. Because bonds mature at regular intervals, investors receive principal repayments periodically, which can be reinvested or used to meet cash flow needs. This can be particularly beneficial for retirees who need reliable income but also want to preserve their capital.
- Diversification of Risk: By spreading investments across different bonds, investors can diversify credit risk. If an investor holds bonds from various issuers, the risk of default by a single issuer has less impact on the overall portfolio. Furthermore, bond ladders can include a mix of government, municipal, and corporate bonds, each with different risk and return profiles.
- Flexibility: Bond laddering offers flexibility in adjusting the investment strategy over time. As each bond matures, the investor can reassess the current economic environment and interest rate trends before reinvesting. This allows for tactical adjustments without having to sell bonds prematurely, which could result in losses.
- Simplifies Management: A bond ladder simplifies the management of a bond portfolio. Instead of trying to time the market by predicting interest rate movements, investors can focus on maintaining their ladder, knowing that the strategy is designed to handle varying interest rate environments.
Implementing a Bond Ladder
To build a bond ladder, investors should first determine the total amount they wish to invest and the range of maturities they are comfortable with. Typically, a ladder includes bonds maturing over a period of 5 to 10 years, but it can be adjusted based on individual goals. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing a bond ladder:
- Assess Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance: Determine how much you want to allocate to bonds and your preferred level of risk. Consider the time horizon for when you will need the funds.
- Choose the Maturities: Select bonds with staggered maturities that fit your investment horizon. For instance, if you plan a 10-year ladder, you might choose bonds that mature in 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 years.
- Diversify the Issuers: Choose bonds from different issuers to spread out credit risk. This might include a mix of government bonds, high-quality corporate bonds, and possibly municipal bonds.
- Monitor and Rebalance: As bonds mature, reinvest the proceeds into new bonds at the top of the ladder. Regularly review your ladder to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and the current economic environment.
Potential Drawbacks
While bond laddering offers many benefits, there are potential drawbacks. In a prolonged low-interest-rate environment, reinvesting maturing bonds could result in lower yields. Additionally, bond laddering requires an initial bonds investment large enough to purchase a diversified set of bonds, which may be a hurdle for some investors.
Conclusion
Bond laddering is a strategic approach to bond investing that provides a structured way to manage interest rate risk, ensure steady income, and maintain flexibility. It simplifies the complexities of bond investing by creating a self-sustaining cycle of maturities and reinvestments. For those looking to balance risk and return in their fixed-income portfolio, bond laddering can be a highly effective strategy.